Blood and Beauty Do Not Mix
Bloodborne pathogen precautions for cosmetologists
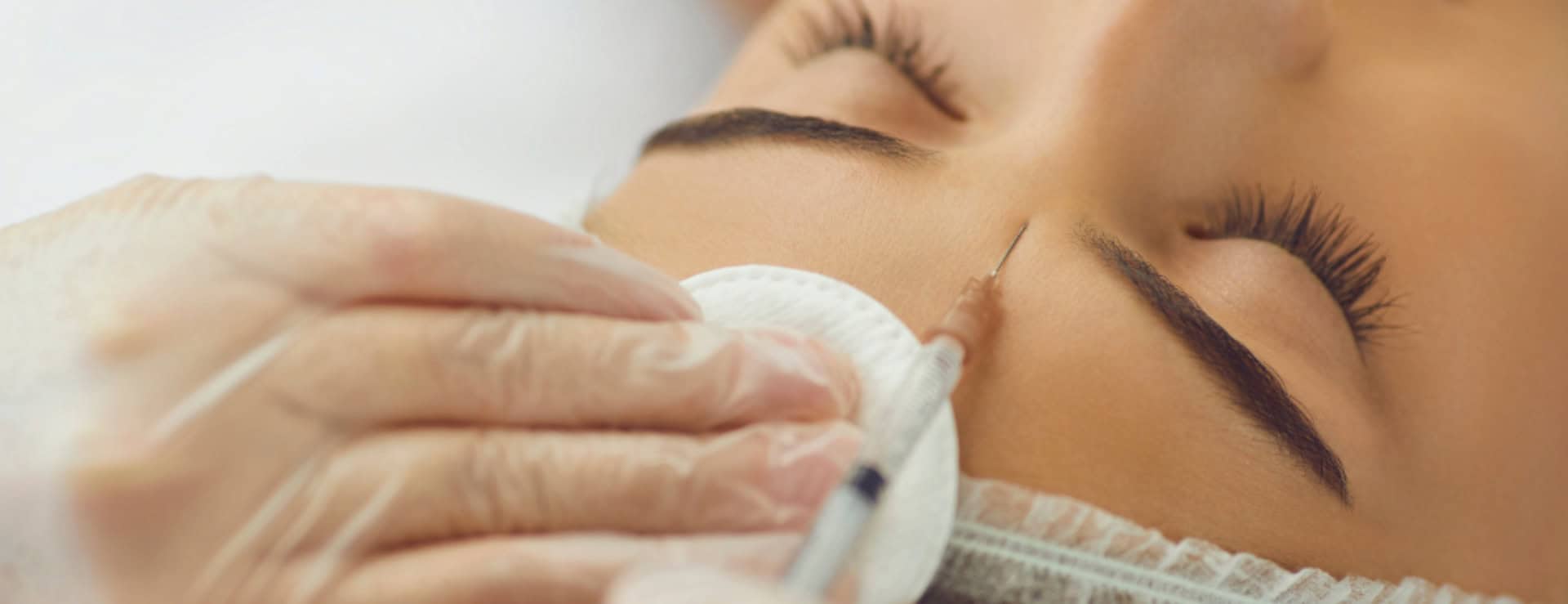
Bloodborne pathogens are disease carrying microbes found in human blood that can cause diseases such as HIV, Hepatitis B and AIDS.
Disease Contraction
If you come in contact with contaminated blood while performing a service at your salon, you can contract disease in one of two ways:
• The infected blood (or other body fluid) can make contact with broken skin, such as a cut or rash.
• The infected blood (or other body fluid) can make contact with a mucus membrane, such as your nose, eyes or mouth.
Since you cannot tell by looking at someone whether he or she is infected with a bloodborne pathogen, treat all blood and other bodily fluids as if they are infectious.
General Precautions
Here are some other precautions to consider:
• Always wear gloves if you must clean up a clients blood when he/she hurts themselves or opens up an existing wound while at the salon.
• Clean and sanitise all work surfaces that were in contact with blood and other bodily fluids immediately.
• Wash your hands immediately after cleaning up or being exposed to blood with soap and warm water.
• Place blood soiled towels and linens in biohazard bags for disposal.
Exposure Recommendations
If another person’s blood or bodily fluid makes contact with your skin or mucus membranes, follow these steps to remain safe:
• Wash your skin with large amounts of soap and warm water.
• Flush the mucus membranes with large quantities of warm water.
• Report the incident to tour supervisor immediately.
• Seek medical care, if necessary.
Be on Guard
It may seem extreme to worry about bloodborne pathogens when working at a beauty salon, but the hazards are real. Exercise tremendous caution when working with clients to protect yourself and your body.
PLAYING IT SAFE HOSPITALITY
Medical Specific Disclaimer:
The following information is not exhaustive, nor does it apply to specific circumstances. The content therefore should not be regarded as medical advice and not be relied upon as such. Readers should contact a medical professional for appropriate advice.
Legal Specific Disclaimer:
The following information is not exhaustive, nor does it apply to specific circumstances. The content therefore should not be regarded as constituting legal or regulatory advice and not be relied upon as such. Readers should contact a legal or regulatory professional for appropriate advice. Further, the law may have changed since the first publication of this information.
Speak to us
